The Gothic Architecture style is one of the world’s most distinctive aesthetically ornate architectural movements which captivates even today. This style of gothic architectural movement originated in the Middle Ages evident in some of Europe’s beautiful churches, cathedrals and other buildings which has been shaped by different influences.
Gothic architecture is characterized by its use of semi-circular arches, ribbed vaults, flying buttresses, and pointed arches, which create an impressive sense of height, light, and space. In this exploration of this unique style of architecture, we will delve into its fascinating history and highlight some of its most renowned examples.
What is Gothic Architecture?
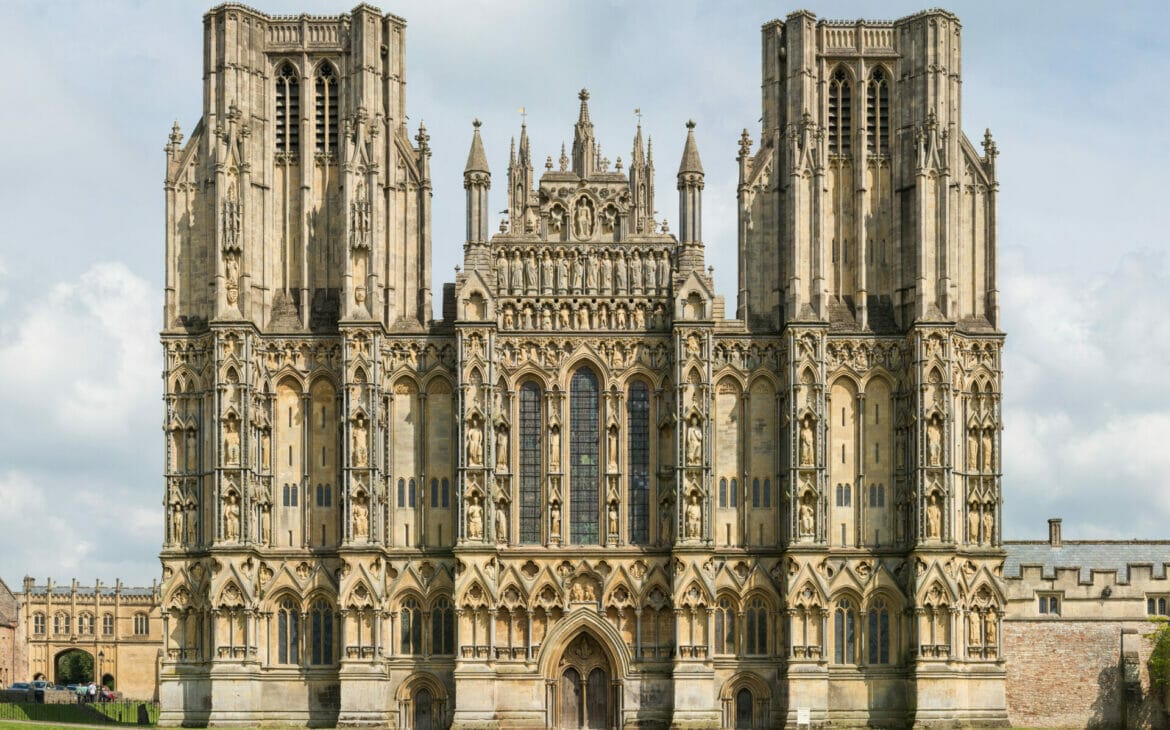

Photo. Wikimedia Commons | Creator: Matthias Zirngibl Buttresses of Strasbourg Cathedral, Strasbourg, France
The Gothic style evolved from Romanesque architecture to produce building which featured exaggerated arches, increased vaulting, and enlarged windows. Gothic architects employed flying buttresses to construct taller, more delicate and intricate sky-high cathedrals with thinner walls which evoked ethereality and reached toward the heavens.
History of Gothic Architecture
It was referred to as Opus Francigenum, or ‘French Work’ till the 16th century after which it became known as ‘Gothic.’ This architecture is divided into three distinct phases: Early, High, and Late each characterized by different design elements, styles, and engineering advancements.
Early Phase
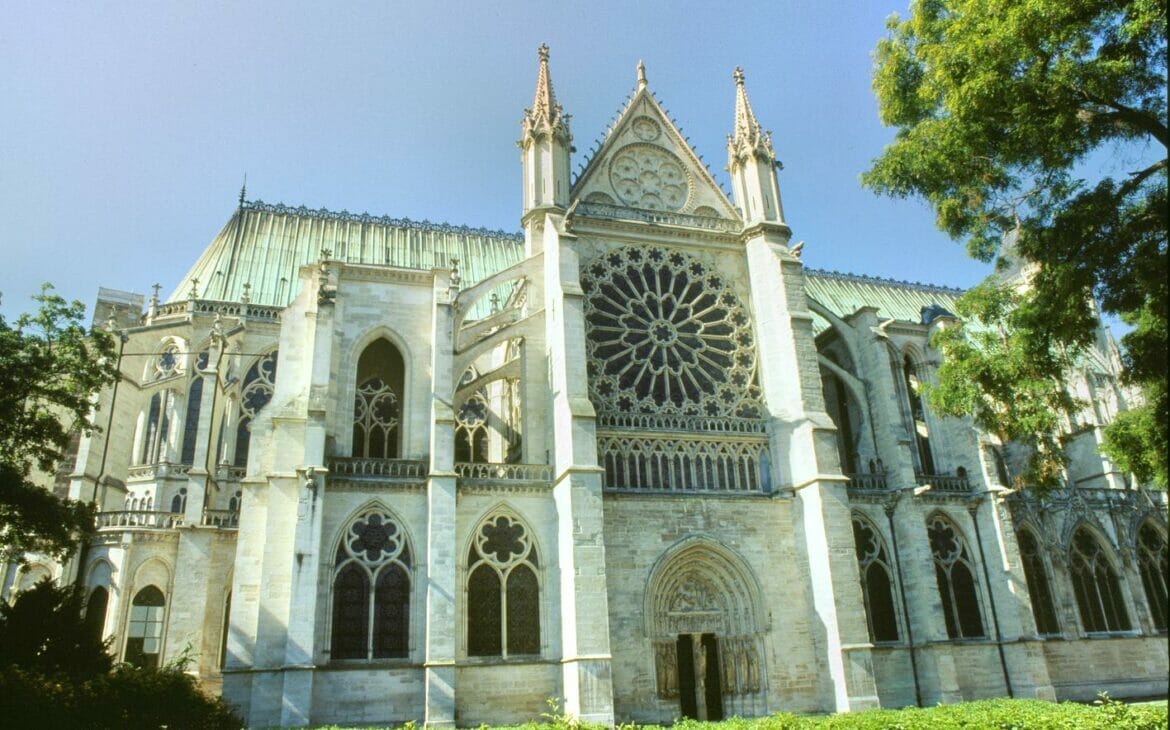

Image Credit: britannica.com
The Early Gothic architecture is the style which originated between 1120 and 1200 in Île-de-France, a region near Paris. This period saw growth and prosperity, as citizens build in the grandiose style as presented by the Abbey of Saint-Denis. Buildings and cathedrals built had four typical distinct levels: a ground-level, tribune gallery level, triforium gallery level, and an upper, windowed level called a clerestory, supported by columns and arches. Windows had decorative dividers and a diverse range of intricate stained glass. This style spread across Europe, appearing in Germany, Italy, Spain, Portugal, and England.
High Phase
The High Gothic era appeared in the 13th century and is referred to as ‘Rayonnant Gothic,’ where Royannant translates into ‘radiant,’ marking a more expressive period with exaggerated decorative styles. Architects approached geometric designs, elaborate adornments, and stylistic enhancements uniquely to construct:-
Pinnacles straight structures on top of piers to give weight to buttresses
Moldings contours or outline edges and surfaces
Window tracey elements in stone supporting the window glass
Mullions vertical or horizontal bars used as decorations
Large, circular rose window which adorned facades of churches for example the iconic rose windows of the Notre Dame Cathedral.
Also Read : What is Brutalist Architecture and why it’s popular?
Late Phase
The Late era is known as ‘Flamboyant Gothic’ architecture or deriving its name from the use of a flame like, s-shaped curve within the window tracery. The architecture of this period was even more decorative compared with the earlier times. New gothic architecture features included the arc en accolade, stone pinnacles, windows decorated with an arch and floral sculptures. One of the most notable example of gothic architecture is the Rouen Cathedral in France, whose construction lasted continued three centuries.
Characteristics of Gothic Architecture
Gothic architecture characteristics are similar to the Romanesque style which prevailed throughout medieval Europe, but avoided the style’s thick walls for delicate walls adding pointed arch, ribbed vault, and flying buttress to create impressive cathedrals and buildings.
Pointed Arch
It opts for a taller, thinner pointed style of arches which can distribute the vault’s weight in a vertical direction, permitting the walls of the cathedral and churches to be thinner. Their silhouette emphasizes the height and symbolically points towards the sky.
Ribbed Vault
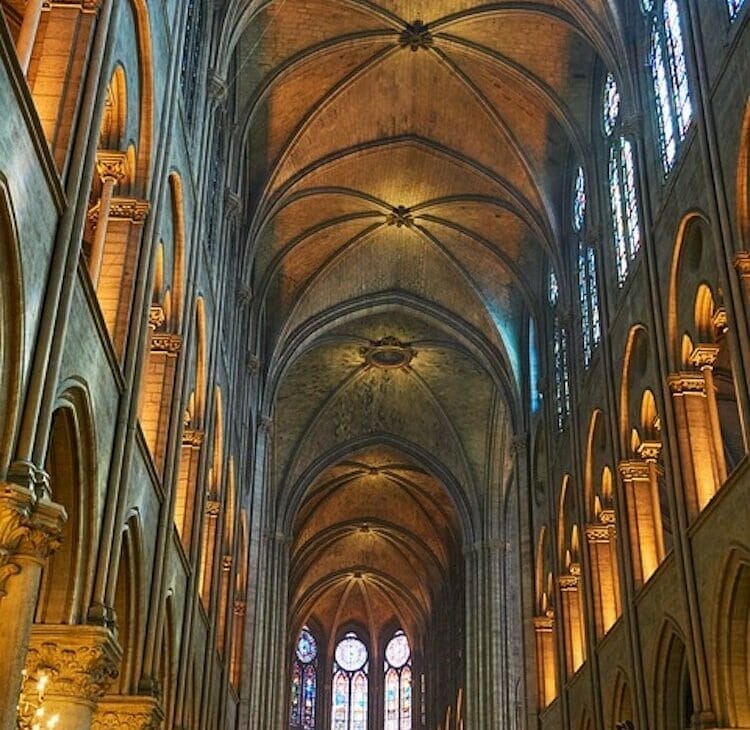

Another feature which defines Collegiate Gothic architecture was the ribbed vault which strengthened the structure of the pointed arch to incorporate higher ceiling and taker windows, and can be seen today in the cathedrals constructed in Ottawa, Canada and other Western countries. Intersecting barrel vaults were used to provide increased structural support. These types of vaults were used in early 13th century in the construction of Amiens and Reims Cathedrals in France. Throughout for aesthetic purpose decorative, ornamental ribs were added to these vaults.
Flying Buttress
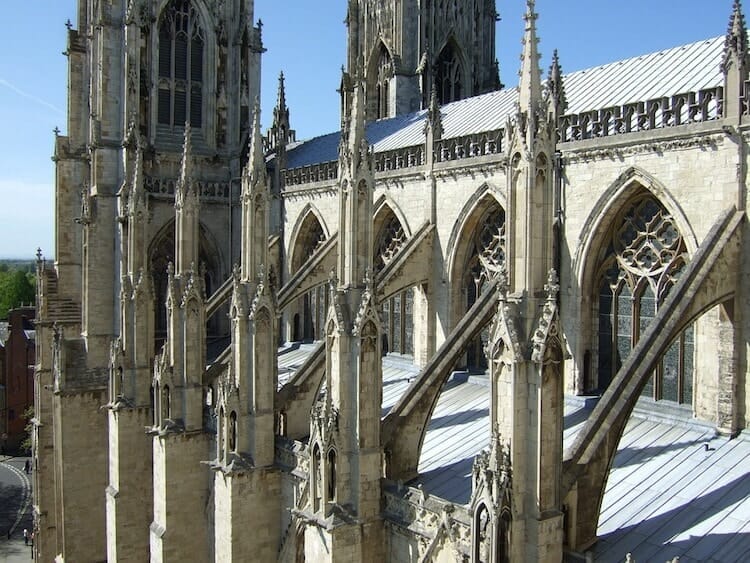

Another revolutionary characteristic was the use of flying buttresses or projecting arched stone structures which extended from the upper portion of walls to piers used to redistribute the weight of the heavy roof to a more solid level. This element helped to achieve tall, exuberant cathedrals which reached towards the skies.
Stained Glass Windows
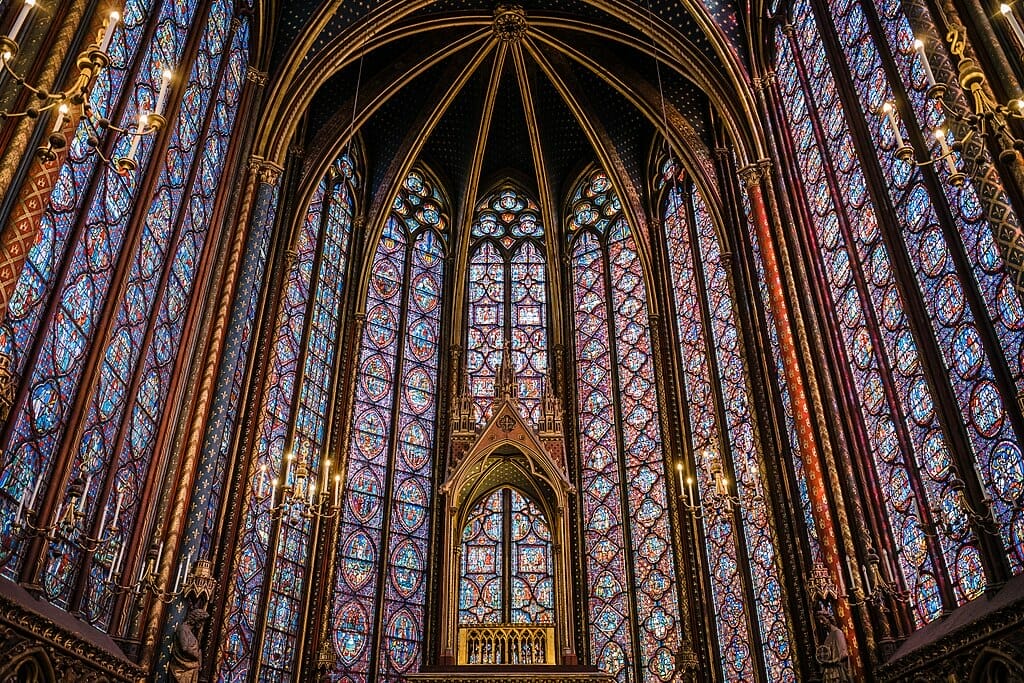
Stained glass windows are a prominent feature prevalent in Gothic cathedrals. These kaleidoscopic windows featured meticulously cut coloured glass—which was either tall and arched ‘lancet’ windows or round ‘rose’ windows—to let in more dazzling light. During this time since literacy was not widespread, the stained glass windows offered worshippers detailed scenes illustrated from Bible in the form of colour and light.
Ornate Decorations
A final feature is the presence of ornate decorative elements which include embellished colonnades and colonettes, statues of saints and historical figures, sculptural mouldings, pinnacles and spires, and gargoyles, grotesque figures which double as water spouts.
Gothic Style Architecture
Gothic Style of Architecture buildings can be found in cities all over France and across Europe. Notable sites in France are Paris’ Notre-Dame Cathedral, Chartres Cathedral, the Basilica of Saint-Denis, Amiens Cathedral, and Reims Cathedral.
There are numerous examples of Gothic architecture around the world, including:
- Notre-Dame de Paris, France – One of the most famous examples of French Gothic architecture, known for its intricate stonework and iconic flying buttresses.
- Westminster Abbey, London, UK – A stunning example of English Gothic architecture, featuring elaborate vaulting and stunning stained glass windows.
- Cologne Cathedral, Germany – A towering example of German Gothic design, with intricate stone carving and stunning towers and spires.
- Sainte-Chapelle, Paris, France – A breathtaking church, renowned for its stunning stained glass windows and ornate Gothic features.
- Chartres Cathedral, France – An iconic structure known for its architecture, ornate decoration and stained glass windows.
- Salisbury Cathedral, UK – A stunning example of English Gothic design, featuring the tallest spire in the UK and elaborate decoration.
- Milan Cathedral, Italy – A magnificent church with Gothic features, including ornate decoration and stunning sculptural detailing.
- Strasbourg Cathedral, France – A towering example of Gothic design, with stunning stained glass windows and ornate stone carving.
- Durham Cathedral, UK – A stunning cathedral featuring intricate stonework and stunning vaulting, built in the Gothic style.
- Burgos Cathedral, Spain -A magnificent example of Spanish Gothic architecture, Burgos Cathedral features ornate decoration and stunning sculptural detailing in the Gothic style.
What are the 7 elements of Gothic architecture?
Pointed arches: This is one of the most distinctive features are Pointed arches are used instead of rounded arches, which were common in Romanesque architecture.
Ribbed vaults: These are vaulted ceilings with a network of ribs that help distribute the weight of the ceiling.
Flying buttresses: These are supports that extend from the exterior of a building to help support the weight of the vaulted ceiling.
Stained glass windows: It is known for its intricate stained glass windows, which often depict scenes from the Bible or other religious stories.
Ornate decoration: It is often highly decorated with intricate carvings, sculptures, and other embellishments.
Towers and spires: Gothic buildings often feature tall towers and spires that reach towards the sky.
Gargoyles: These are decorative features that serve as water spouts on the exterior of a building. They often take the form of grotesque creatures such as demons, monsters, or animals.























